
Get blood tests as advised by your provider to make sure you are taking the right dose.Ask the provider what to do if you miss a dose.Take the medicine just the way your provider prescribed it.If you are taking a blood thinner at home: When you are taking a blood thinning medicine, you are more likely to bleed, even from activities you have always done. Some people take it longer, or even for the rest of their lives, depending on their risk for another clot. You will most likely take a blood thinner for at least 3 months. Your provider will decide which medicine is right for you. These drugs work in a similar way to heparin and can be used right away in place of heparin. Examples of this class of medicines, called direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC), include: It takes several days to fully work.Īnother class of blood thinners works differently than warfarin. One type of blood-thinning medicine called warfarin (Coumadin or Jantoven) may be started along with heparin. You may not need to stay in the hospital as long, or at all, if you are prescribed this type of heparin.
Deep vein thrombosis arm skin#
Low molecular weight heparin can be given by injection under your skin once or twice a day.However, most people can be treated without staying in the hospital. If heparin is given through a vein (IV), you must stay in the hospital.Heparin is often the first medicine you will receive. This will keep more clots from forming or old ones from getting bigger. Your provider will give you medicine to thin your blood (called an anticoagulant). This is most likely when you also have one or more of the risk factors listed above. Sitting for long periods when traveling can increase the risk for DVT. Taking estrogens or birth control pills (this risk is even higher with smoking).Conditions that make it more likely to develop blood clots.Certain autoimmune disorders, such as lupus.Having an indwelling (long-term) catheter in a blood vesselīlood is more likely to clot in someone who has certain problems or disorders, such as:.Too many blood cells being made by the bone marrow, causing the blood to be thicker than normal ( polycythemia vera).Recent surgery (most commonly hip, knee, or female pelvic surgery).Bed rest or sitting in one position for too long, such as plane travel.A pacemaker catheter that has been passed through the vein in the groin.An embolism can get stuck in the blood vessels in the brain, lungs, heart, or another area, leading to severe damage.īlood clots may form when something slows or changes the flow of blood in the veins. When a clot breaks off and moves through the bloodstream, it is called an embolism. After proper diagnosis, the vascular specialists at Horizon will ensure your treatment is customized to your needs.DVT is most common in adults over age 60. Whether your DVT requires treatment with medications or minimally invasive procedures. Post thrombotic syndrome is characterized by chronic swelling, pain, and in its worst form ulceration. In some cases of more extensive DVT involving the iliac veins or common femoral veins more aggressive treatment has been recommended to remove the clot to prevent post thrombotic syndrome.

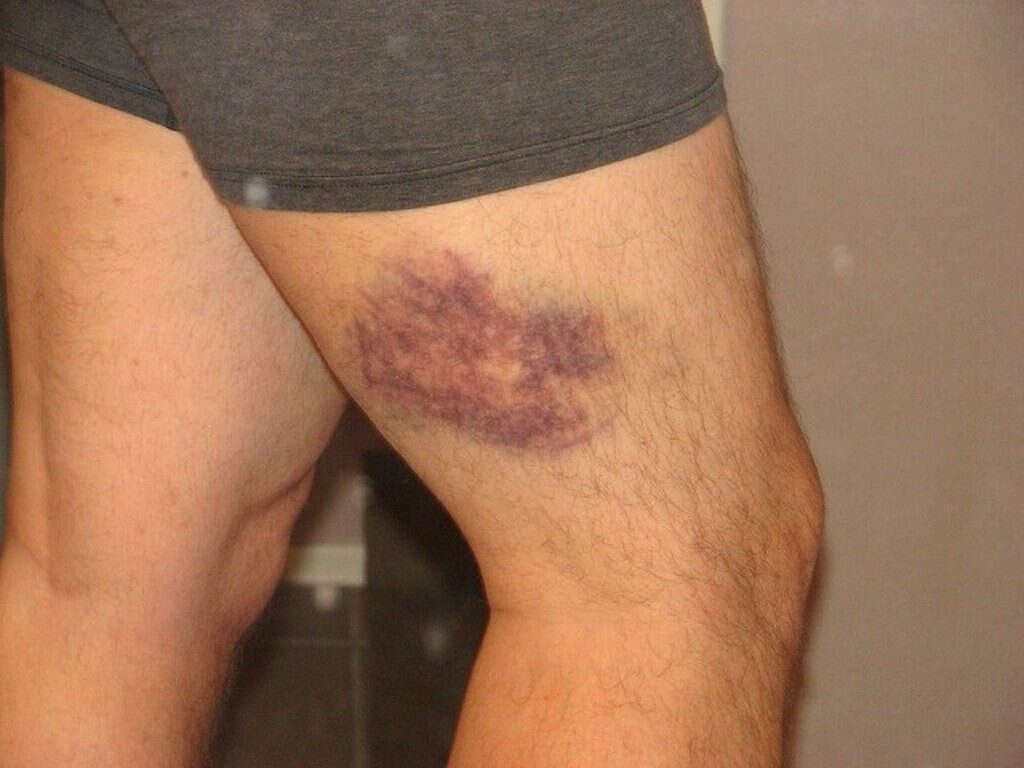
However, in about half the cases, there are mild to no symptoms at all. DVT can block blood flow, causing leg pain or swelling (edema), tenderness, skin redness, or a sensation of warmth. It can sometimes be difficult to recognize the symptoms of DVT.

DVT can lead to serious, life-threatening complications, such as a pulmonary embolism. DVT occurs most commonly in your lower leg and thigh but can occasionally occur in your arm, chest, or other areas of the body. These deep veins lead to the body’s largest vein called the vena cava, which runs directly to the heart. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in one or more of the deep veins in your body.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
